2026 Top Submersible Well Pump Technologies for Water Solutions?
In today's world, finding efficient water solutions is crucial. The submersible well pump industry plays a pivotal role in this challenge. John Smith, a leading expert in water technologies, states, “Innovations in submersible well pump design can transform access to clean water.” His insights guide the focus on 2026’s top technologies.
Submersible well pumps are essential for accessing groundwater. They operate underwater, making them more efficient than traditional pumps. However, not all models are effective. Some designs face issues with energy consumption and durability, often reflecting poor craftsmanship. Continuous advancements aim to resolve these shortcomings.
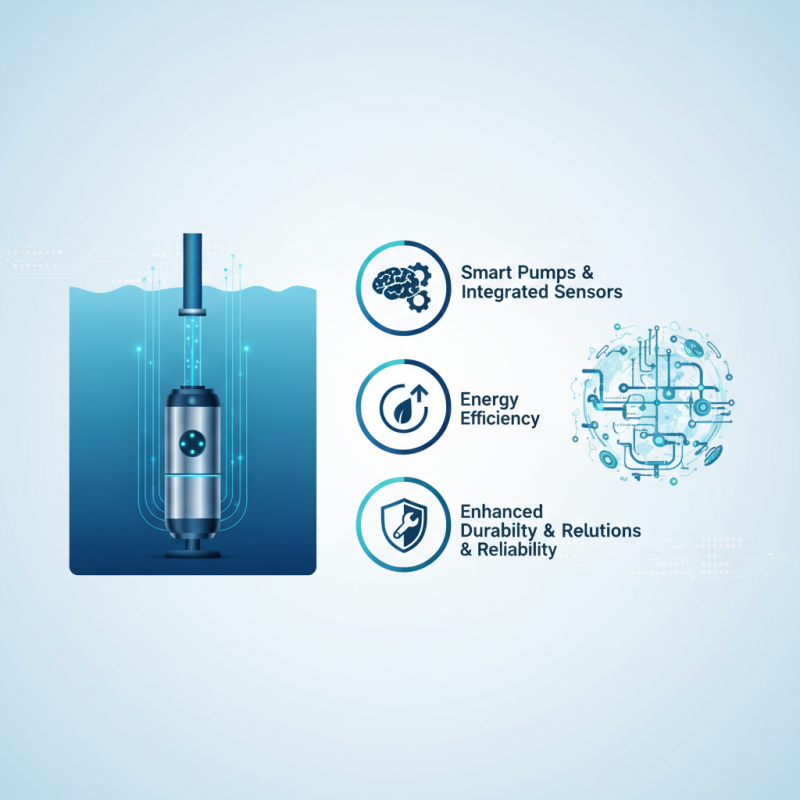
Emerging technologies promise enhanced performance and lower operational costs. Smart pumps with integrated sensors are on the horizon. They could improve monitoring and maintenance. The landscape is evolving, yet challenges remain. It is vital to carefully assess not just new features but also reliability. As the demand for clean water grows, so must our scrutiny of submersible well pump technologies.

Overview of Submersible Well Pump Technologies
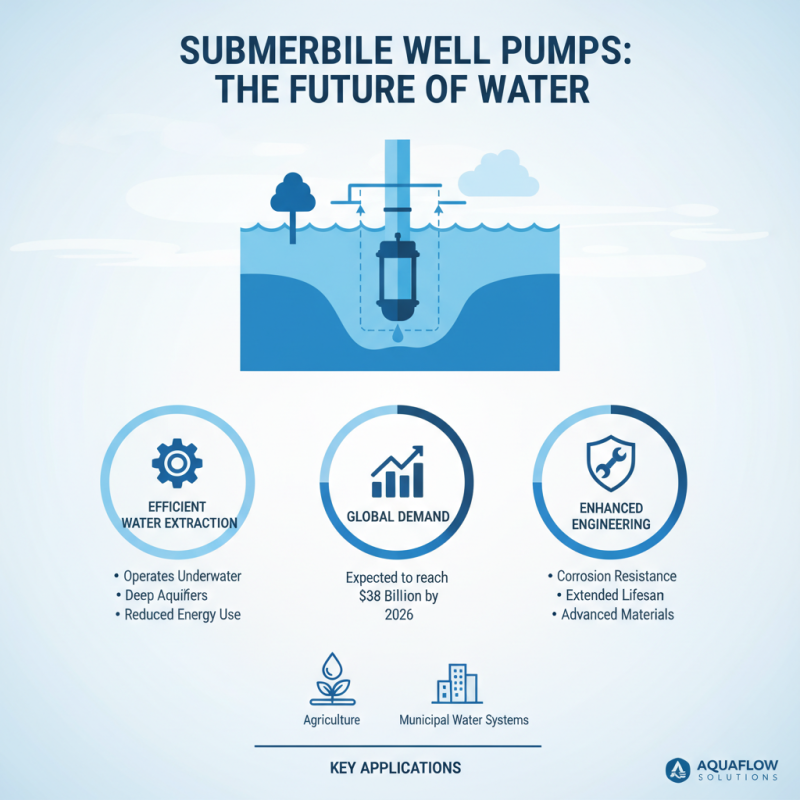
Submersible well pumps are crucial for efficient water extraction. They operate underwater, allowing them to draw water from deep aquifers. This technology is gaining traction, especially in agriculture and municipal water systems. Reports suggest that global demand for submersible pumps could reach $38 billion by 2026. Enhanced engineering continues to address issues like corrosion and wear, which affect pump lifespan.
Recent innovations include improved motor designs and smart technology integration. Advanced sensors can monitor performance and detect issues in real-time. These updates have resulted in more reliable operation. However, challenges remain. Older designs often fail under increased pressure, leading to costly replacements. Many systems still lack proper maintenance protocols.
Efficiency is another area needing attention. While some pumps achieve an impressive 85% efficiency, others lag significantly. This inconsistency fosters unnecessary waste. Many users still overlook the importance of selecting the right pump for their specific needs. It’s crucial for sustainability and long-term savings. The industry must continue evolving, prioritizing user education and proper implementation of new technologies.
Key Innovations in Submersible Pump Design for 2026
In 2026, submersible pump technology will see significant advancements. The focus will shift towards energy efficiency and sustainability. New materials are being tested, such as composite and corrosion-resistant options. These materials can enhance durability, especially in harsh environments.
Innovative designs will also play a crucial role. For instance, multiple impeller configurations are being explored. These designs can improve flow rates and reduce energy consumption. Additionally, smart sensors are becoming more commonplace. They track performance metrics in real time and streamline maintenance schedules. However, integrating these technologies can be challenging, and not all pumps will adapt seamlessly.
Environmental considerations are becoming essential in pump design. Engineers are looking to reduce noise pollution and minimize energy waste. However, a balance between performance and ecological impact must be found. As demand grows, it’s vital to reflect on these innovations. What works for one setting might not be best for another. Each solution must be carefully evaluated for effectiveness.
Environmental Impact of Advanced Submersible Pump Solutions
Advanced submersible pump technologies are transforming water management. These innovations promise efficient water extraction and waste minimization. The environmental impact is a major consideration. We need to assess how these pumps affect groundwater levels and aquatic ecosystems.
New designs focus on energy efficiency. They reduce electricity use and lower greenhouse gas emissions. However, we must explore the trade-offs. Over-extraction may lead to depleted water sources. Additionally, some materials used in pumps could release harmful substances into water bodies.
Community feedback is crucial in this process. Are these technologies meeting local needs without causing harm? People living near extraction sites often observe ecological changes. Their insights can guide better practices. We must strive for solutions that not only enhance efficiency but also promote sustainability. Balancing technology and nature is challenging. Continuous evaluation is necessary to avoid unintended consequences.
2026 Top Submersible Well Pump Technologies for Water Solutions
Comparative Analysis of Leading Submersible Pump Brands
In recent years, submersible well pumps have transformed water solutions across various sectors. The market is filled with numerous pump brands, each claiming superior performance. However, a comparative analysis reveals distinct advantages and drawbacks among them.
Efficiency is a primary factor. Some pump technologies excel in energy consumption. Others may offer higher flow rates but at the cost of increased power use. Balancing these factors can be challenging. Durability also plays a significant role. Certain pumps withstand extreme conditions, while others fail prematurely under similar stress. Users often face tough decisions regarding which specifications matter most for their specific needs.
Maintenance is another critical area. Some models require minimal care, leading to lower operational costs. In contrast, others demand regular servicing, which can be burdensome. This brings up the need for thorough evaluation. Understanding user experiences can shed light on long-term reliability. Investing time in research will help make informed choices. Often, the best option is not immediately obvious, and trial and error may be necessary.
Future Trends in Submersible Well Pump Applications and Technology
The landscape of submersible well pumps is evolving rapidly. Future applications focus on efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability. Water scarcity issues loom large, making advanced pump technology crucial. Innovative designs integrate smart sensors that provide real-time data. This advancement helps users manage water resources better and minimize waste.
Additionally, eco-friendly materials are becoming more prominent. These materials promise not only durability but also reduced environmental impact. However, this shift requires balancing performance and cost. Implementing cutting-edge technology may lead to higher initial investments. It’s essential to evaluate these trade-offs and determine long-term benefits.
The trend toward renewable energy sources is also taking shape. Solar-powered submersible pumps could revolutionize water supply in remote areas. Still, challenges remain in ensuring consistent power generation. The reliability of these systems needs thorough consideration. As technology progresses, ongoing reflection and adjustment will be necessary.
2026 Top Submersible Well Pump Technologies for Water Solutions
| Technology Type | Efficiency (%) | Applications | Depth Capability (m) | Material Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | 85-95 | Agriculture, Municipal | 150 | Stainless Steel |
| Solar Submersible Pumps | 75-85 | Remote Areas, Irrigation | 100 | Plastic, Stainless Steel |
| Submersible Turbine Pumps | 80-90 | Industrial, Mining | 300 | Cast Iron, Stainless Steel |
| Smart Pump Technology | 90-95 | Smart Cities, Automation | 200 | Composite Materials |
| Electric Submersible Pumps (ESP) | 80-88 | Oil Extraction, Water Supply | 400 | Steel, Composite |
Related Posts
-

Exploring Market Trends for Submersible Dirty Water Pumps at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Needs
-

2025 Top 10 Submersible Dirty Water Pumps for Effective Waste Management
-

How to Choose the Right Submersible Pump for Your Needs: A Complete Guide
-

Transform Your Garden: The Ultimate Guide to Submersible Water Pumps for Efficient Irrigation
-

Choosing the Right Submersible Pump: Key Specs and Insights to Boost Your Efficiency