How to Choose the Right Borehole Pump for Your Water Needs
When it comes to sourcing water for agricultural, industrial, or personal use, selecting the right borehole pump is crucial to ensuring efficiency and reliability. Borehole pumps are specifically designed to extract water from deep underground sources, making them essential for users who require consistent access to water. However, the variety of borehole pumps available on the market can be overwhelming, prompting many to question how best to identify the one that suits their unique water needs.
Understanding the different types of borehole pumps and their respective features is vital in making an informed decision. Factors such as the pump's depth, flow rate, material construction, and energy source play significant roles in determining the most appropriate option for your situation. Whether you are a farmer looking to irrigate crops or a homeowner wanting to ensure a steady water supply, the right borehole pump can drastically impact efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This guide aims to simplify the selection process by providing essential insights into the key considerations when choosing a borehole pump tailored to your specific requirements.

Understanding Borehole Pumps and Their Applications
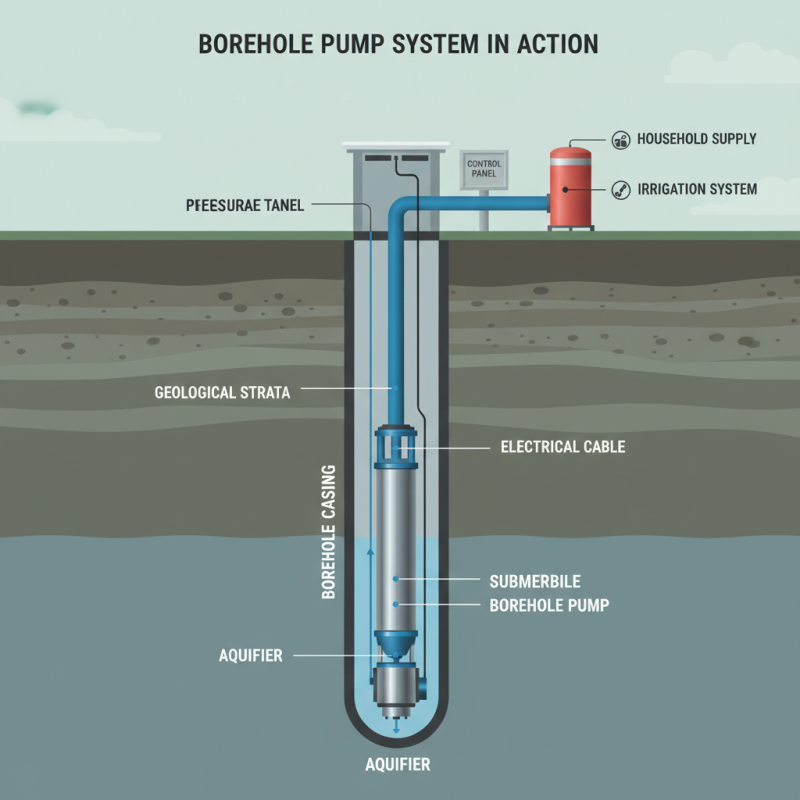
Borehole pumps are specialized devices designed to extract water from deep underground sources, making them essential for various applications, including residential, agricultural, and industrial use. Understanding the different types of borehole pumps is crucial for selecting the right one for your specific needs. These pumps can vary significantly in size, capacity, and design, so it’s important to have a clear understanding of your water requirements and the depth of the borehole when selecting a pump.
Applications for borehole pumps extend beyond just extracting water for irrigation or domestic use. They are also widely used in industrial settings for supplying water for cooling systems and in municipal settings for supplying clean water to communities. Each application may have unique requirements, demanding different pump specifications, such as flow rate and total dynamic head. By assessing the intended use and understanding the characteristics of the pump, users can ensure efficient operation, optimal performance, and longevity of the pump system.
Assessing Your Water Needs and Flow Requirements
Assessing your water needs and flow requirements is a critical step in selecting the right borehole pump. Start by determining the volume of water you require daily. Consider your usage scenarios such as household consumption, irrigation, or industrial needs. You might have varying demands based on seasonality—higher water needs during dry months or increased usage in summer for gardens. Calculating your average daily consumption will provide a baseline to work from.
Next, evaluate the flow rate you’ll need from the pump. This is typically measured in liters per minute (L/min) or gallons per minute (GPM). The flow rate should match not only your daily consumption but also your peak usage times. For instance, if you plan to irrigate a large area simultaneously, the pump must be capable of delivering enough water to meet this demand without interruption. Additionally, consider how deep the water source is, as this influences the pump's size and power requirements. Understanding both the daily volume and flow rate will guide you in choosing a borehole pump that efficiently meets your specific water needs.
Evaluating Different Types of Borehole Pumps
When evaluating different types of borehole pumps, it's essential to understand the various options available and their suitability for your specific water needs. Borehole pumps can be broadly categorized into submersible pumps and jet pumps, each designed for different applications. Submersible pumps, often used for deeper installations, are submerged in the water and push water to the surface, making them efficient for high-flow situations. Conversely, jet pumps, which can be above ground, use suction to draw water from a borehole and are typically used in shallower installations.
Another critical aspect to consider is the material and construction of the borehole pump. Pumps are often made from stainless steel, plastic, or cast iron, each offering varying levels of durability and resistance to corrosion. For instance, stainless steel is ideal for applications where water quality might affect the pump's longevity, while plastic can be effective in less demanding environments.
Additionally, the pump's flow rate and head pressure capabilities are essential factors to ensure that the pump can meet the required water output for your particular needs, especially in agricultural or residential applications. By carefully assessing these different types of borehole pumps and their features, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your water requirements.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Borehole Pump
When selecting the right borehole pump for your water needs, several critical factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. First and foremost, you need to assess the pump's flow rate, which refers to the volume of water the pump can deliver over a specific period. Industry reports indicate that residential borehole pumps typically require flow rates ranging from 5 to 30 gallons per minute (GPM), depending on usage patterns and demand. Calculating the total water demand of your household or agricultural application can help inform the necessary flow rate you should aim for, ensuring you meet your needs without overloading the system.
Another essential factor is the borehole depth, which impacts the type of pump required. A submersible pump, for instance, is designed for deeper installations and can operate efficiently at depths of 30 feet or more. According to research by the International Water Management Institute, it is vital to determine the water table level and the depth of the borehole accurately before making a purchase. In addition, the total dynamic head (TDH) of the pump—which includes the vertical lift and the friction losses in the piping system—should be calculated. This TDH requirement will ultimately help identify a pump with the right power and motor specifications, ensuring that you achieve reliable water delivery throughout your use phase.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Borehole Pumps
When it comes to installing a borehole pump, proper preparation and adherence to guidelines are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Begin by selecting an appropriate site with good accessibility to facilitate maintenance activities. Ensure that the borehole is properly drilled and water quality tests are conducted to understand the water chemistry, which can influence the pump's performance. During installation, double-check the alignment of the pump and piping to avoid unnecessary strain, and make sure all electrical connections are secure and waterproof to prevent failures due to moisture.
Maintenance of a borehole pump is crucial for sustaining its efficiency. Regularly inspect the pump for signs of wear or damage, and establish a routine schedule for cleaning filters and screens to prevent clogging, which can reduce flow rates. Test the pump's performance periodically to identify any drop in output or efficiency, as this may indicate potential issues such as motor degradation or impeller damage. Additionally, maintain proper water levels in the borehole to prevent the pump from running dry, which can significantly shorten its lifespan. Adopting these practices will help ensure that your borehole pump operates effectively and serves your water needs reliably over time.
Water Needs Analysis for Borehole Pumps
Related Posts
-

Transform Your Garden: The Ultimate Guide to Submersible Water Pumps for Efficient Irrigation
-

How to Choose the Right Submersible Pump for Your Needs: A Complete Guide
-

Top 10 Dirty Water Pumps: Efficient Solutions for Heavy-Duty Water Removal in 2023
-
Exploring Water Pump Innovations for Home Use at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Dewatering Pump for Your Needs
-

Why Water Pump Price Matters: Understanding Costs for Your Needs