2025 How to Choose the Best Dewatering Pump for Your Needs
In the world of water management and construction, selecting the right dewatering pump can be a critical decision that impacts both project efficiency and cost-effectiveness. As we approach 2025, understanding the latest advancements in dewatering technology becomes increasingly important. Industry expert John Smith, a recognized authority in fluid management systems, emphasizes, "Choosing the right dewatering pump is not just about capacity; it's about understanding your specific needs and the environmental conditions."
The variety of dewatering pumps available on the market can be overwhelming, with different models designed for varying applications, including construction sites, mining operations, and municipal projects. Each situation demands a tailored approach to ensure optimal performance, which hinges on factors such as pump type, flow rate, and total dynamic head. With the right knowledge, you can make informed choices that enhance your project's success while minimizing potential pitfalls.
As we explore the top five dewatering pumps of 2025, we aim to equip you with insights that will help navigate this critical decision-making process. With the perspectives of experts like Smith and a focus on current trends, we will highlight essential features and considerations to ensure you select the best dewatering pump for your unique requirements.

Understanding the Different Types of Dewatering Pumps Available in the Market
When selecting the best dewatering pump for specific needs, it’s crucial to understand the various types available in the market. The dewatering pump segment is expected to reach USD 10.0 billion by 2035, demonstrating a steady growth rate of 2.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035. This growth is driven by diverse sectors requiring efficient water removal solutions, particularly in construction and mining industries where unplanned water ingress can significantly disrupt operations.
The North America utility pump market showcases a variety of products, including transfer pumps, submersible pumps, and specifically dewatering pumps. Each type serves different applications; for instance, submersible pumps are particularly effective in areas with deep water levels, while transfer pumps are ideal for moving water over short distances. As the mining pumps market is projected to reach USD 4.8 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 4.9%, the demand for specialized dewatering solutions is anticipated to increase, tailor-fitting to the requirements of these industries. Understanding the nuances of each type helps in making informed decisions for effective water management.
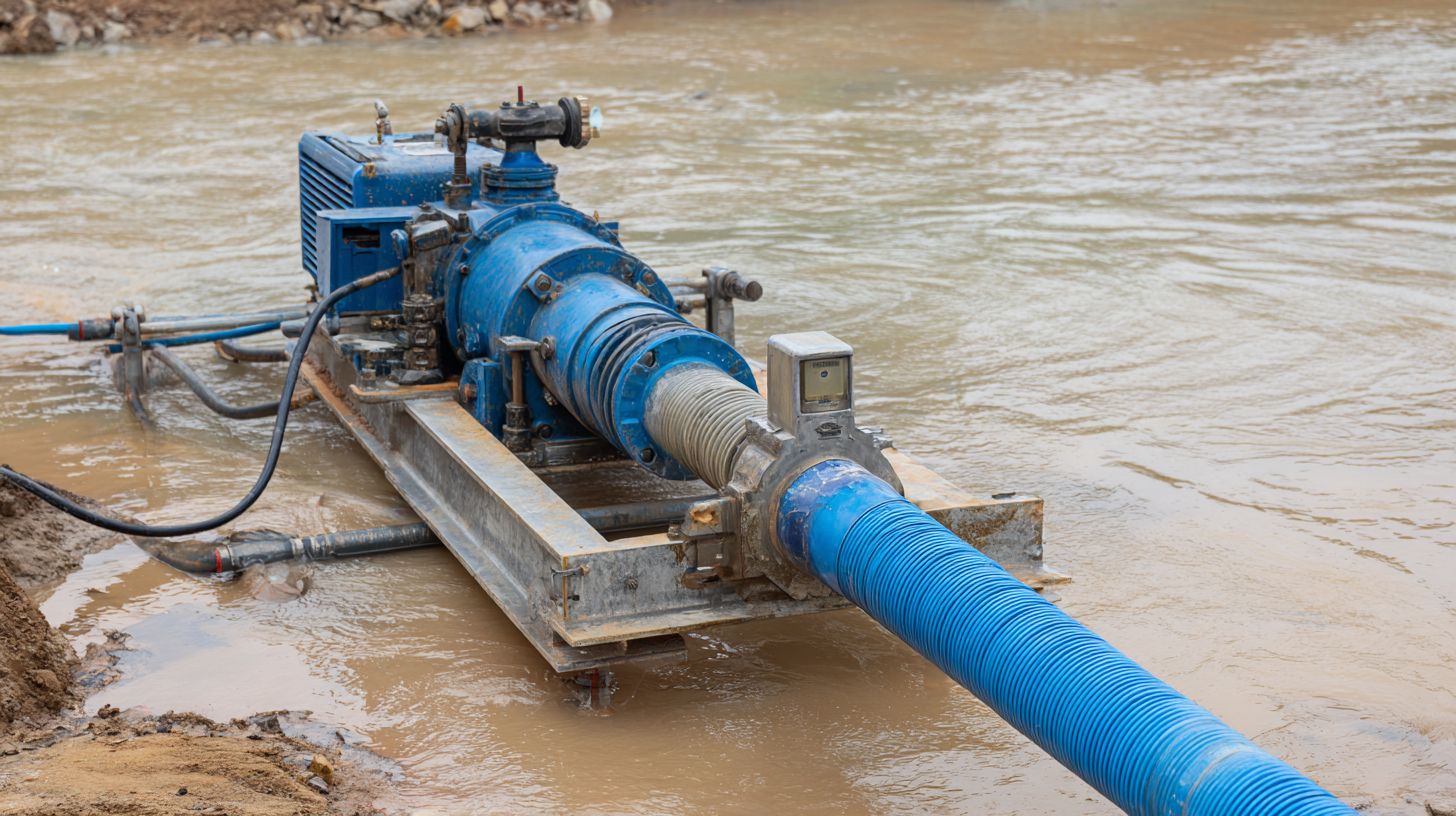

Key Factors to Consider When Selecting the Right Dewatering Pump
When selecting the right dewatering pump, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance for your specific needs. First, assess the type of water you will be pumping—clear water, dirty water, or even hazardous liquids—as this impacts the pump's design and material composition. According to a report from the Global Market Insights, the dewatering pump market is projected to grow significantly, emphasizing the importance of choosing a pump that meets industry standards and can handle the specific contaminants in your project.
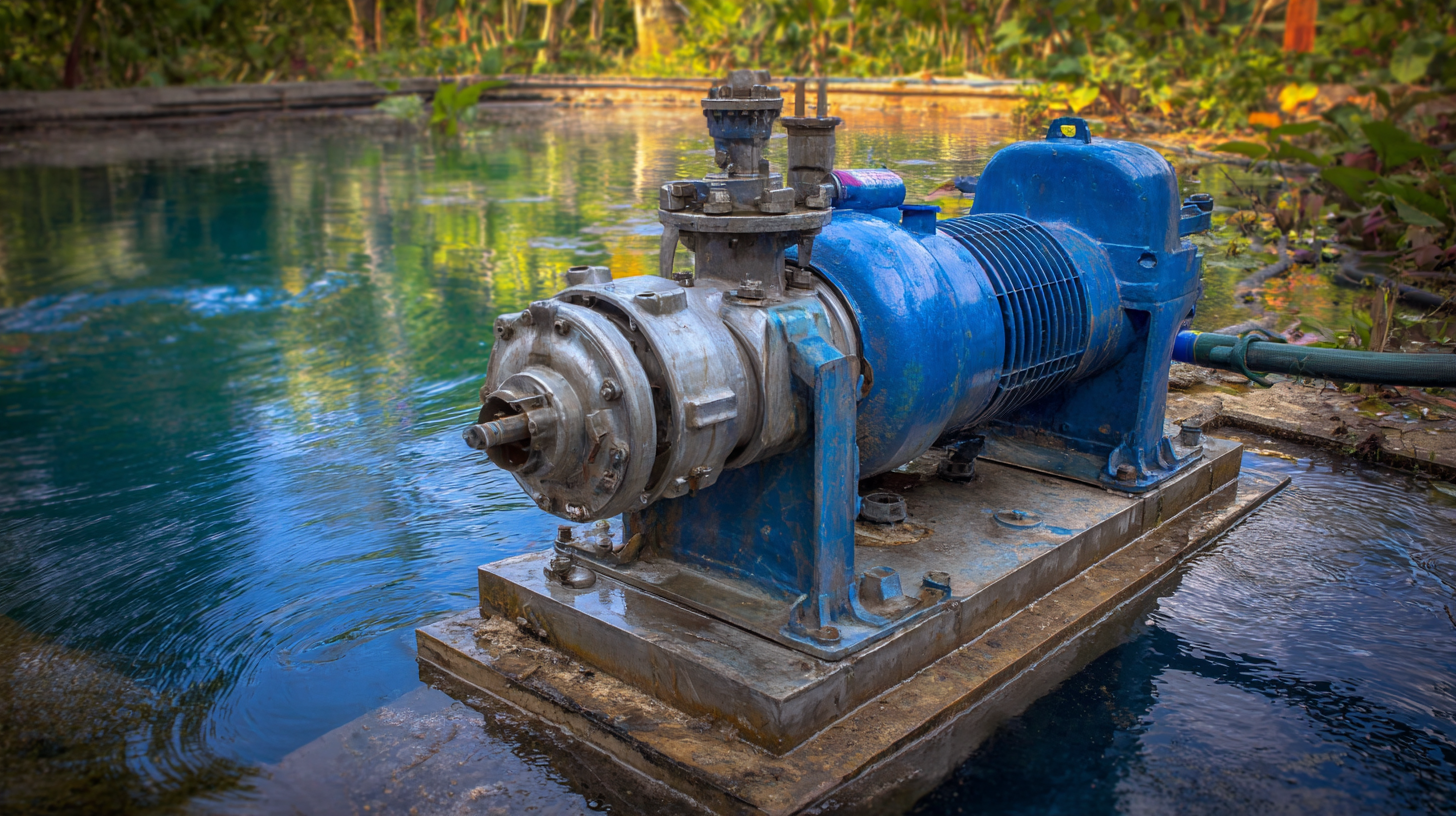

Another crucial factor is the pump's capacity and head, which refer to the volume of water it can move and the height it can lift, respectively. For example, if you are working on a construction site, a pump with a higher flow rate will be necessary to efficiently manage large volumes of water. A comparative analysis of pump specifications can reveal that by upgrading to a higher-capacity model, users can achieve a 20% increase in efficiency, directly influencing project timelines and costs.
Tips: Always consider the total dynamic head (TDH) when selecting a pump, as it is integral to the pump's performance in real-world conditions. Investing in a model with adjustable settings can provide additional flexibility for varying applications. Lastly, consult with industry professionals for tailored advice; they can share insights on the most reliable brands and models based on extensive market research and user feedback.
Comparing Submersible vs. Non-Submersible Dewatering Pumps for Your Needs
When it comes to dewatering pumps, choosing between submersible and non-submersible options can significantly impact efficiency and functionality. The submersible pump market is projected to reach a valuation of $15.5 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for effective water management solutions. These pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them ideal for tasks like draining flooded areas or managing groundwater. Their ability to handle high flow rates—up to 20,000 liters per minute—while operating at depths of up to 85 meters adds to their appeal for industrial applications.
In contrast, non-submersible pumps, often used for surface draining, may have limitations in terms of head pressure and flow rates compared to their submersible counterparts. The growing trend of innovative dewatering solutions in North America signals a shift toward more efficient systems tailored to distinct operational needs. With market forecasts indicating a robust growth trajectory, understanding the specific requirements for your dewatering projects is essential to making an informed decision.
2025 How to Choose the Best Dewatering Pump for Your Needs - Comparing Submersible vs. Non-Submersible Dewatering Pumps
| Feature | Submersible Pump | Non-Submersible Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Environment | Can operate underwater | Must be above the fluid level |
| Installation | Easy installation in confined spaces | Requires additional plumbing |
| Efficiency | High efficiency when submerged | Good for large volumes of water |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection | Easier access for repairs |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Typically lower initial cost |
| Common Applications | Construction sites, basements | Draining large tanks, water removal |
Assessing Pump Performance: Flow Rate, Head Height, and Efficiency
When selecting a dewatering pump, understanding key performance metrics such as flow rate, head height, and efficiency is essential. The flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), indicates how much water a pump can move within a given timeframe. A higher flow rate is crucial for tasks requiring rapid water removal, such as in construction sites or flood response. However, it's important to match the flow rate with your specific needs to avoid oversizing the pump, which can lead to unnecessary energy consumption.
Head height, or total dynamic head (TDH), measures the height a pump can lift water. This is particularly significant when pumping water vertically, as it influences the pump's overall performance. Each dewatering application may have different head height requirements, depending on the setup and location of the water source. When evaluating pumps, ensure that the specified head height aligns with your project conditions; this will prevent inefficiencies and potential equipment failure. Coupled with these factors, pump efficiency, often expressed as a percentage, plays a critical role in minimizing operational costs while maximizing performance over time. Selecting a pump with high efficiency can lead to sustainable usage, saving both energy and money in the long run.
Budgeting for Your Dewatering Pump: Cost Considerations and Value Analysis
When selecting a dewatering pump, budgeting is a crucial step that can significantly impact your overall investment. Start by determining your specific needs, including the volume of water to be moved and the type of project. This will help you establish a baseline for the cost of the pump itself. Prices can range widely based on factors such as brand, power type, and pump capacity, so it’s important to compare options and understand what features are essential for your application.
In addition to the initial purchase price, consider the lifetime costs associated with the pump. These may include maintenance, energy consumption, and potential repair costs. Analyzing these factors can provide a clearer picture of the value offered by different models. Opting for a slightly higher-priced, more efficient pump may ultimately save money in the long run through reduced operational costs. By thoroughly assessing both the upfront and ongoing expenses, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your budget while ensuring the pump meets your dewatering needs effectively.
2025 Dewatering Pump Cost Considerations
Related Posts
-

Exploring Market Trends for Submersible Dirty Water Pumps at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding How Water Pumps Transform Our Daily Lives
-

Top 10 Dirty Water Pumps: Efficient Solutions for Heavy-Duty Water Removal in 2023
-

Transform Your Garden: The Ultimate Guide to Submersible Water Pumps for Efficient Irrigation
-

Unlocking the Power of Small Electric Water Pumps: Your Ultimate Guide to Efficient Water Solutions
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Small Water Pumps in Everyday Life and Gardening