What is a Small Pump and How Does It Work in Various Applications
In an era where efficiency and compactness are paramount, the small pump has emerged as a vital component across various industries. Defined as pumps with a capacity generally under 500 gallons per minute, small pumps are employed in applications ranging from water treatment and agricultural irrigation to medical devices and HVAC systems. According to a recent market report by Grand View Research, the global small pump market is projected to exceed $20 billion by 2025, driven by advancements in technology and the rising demand for energy-efficient systems.
The versatility of small pumps is further emphasized by their adaptability to work in diverse environments. For instance, in the agricultural sector, small submersible pumps are crucial for managing water resources effectively, improving irrigation efficiency, and supporting sustainable farming practices. In the healthcare field, the precision of small pumps ensures accurate fluid delivery, which enhances patient care and treatment outcomes. As industries continue to innovate and seek compact yet powerful solutions, the role of small pumps will undoubtedly expand, making them indispensable in meeting modern demands and addressing global challenges.

Definition and Characteristics of Small Pumps

Small pumps are essential devices designed to move fluids in various applications, including wastewater management, agricultural irrigation, and medical equipment. Typically characterized by their compact size and efficiency, small pumps can handle a range of fluids from water to viscous substances. According to the Global Market Insights report, the small pump market is projected to exceed $10 billion by 2026, driven by growing demand in industrial and domestic sectors.
These pumps can be classified based on their design and operating principles, such as centrifugal or positive displacement pumps. Centrifugal pumps utilize rotational energy, making them ideal for high-capacity applications, while positive displacement pumps can effectively manage thicker fluids by trapping a fixed amount of liquid and forcing it out. Their versatility and reliability make small pumps vital not only for industrial processes but also for everyday applications like aquariums and home heating systems.
**Tips:** When selecting a small pump, consider factors like flow rate, head height, and the type of fluid being pumped to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance, such as checking for leaks and replacing worn seals, can prolong the lifespan of the pump, ensuring it operates efficiently across various applications.
Types of Small Pumps and Their Operating Principles
Small pumps are essential devices used in various industries, from agriculture to pharmaceuticals. They come in several types, each designed to meet specific operational needs. The two primary categories include positive displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global small pump market is expected to reach USD 5.7 billion by 2024, highlighting their significance across diverse applications.
Positive displacement pumps operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it into the discharge pipe. This type is particularly beneficial in applications requiring precise flow rates, such as metering in chemical processes. On the other hand, centrifugal pumps leverage rotational energy from a motor to move fluids. The centrifugal force generated by the impeller translates into increased fluid velocity, making them ideal for high-volume water transfer tasks, as reported by Research and Markets, which indicates a steady growth in demand for these pumps in irrigation systems.
Understanding the operational principles and applications of various small pumps allows industries to optimize their processes effectively. In sectors like aquaculture, for example, small pumps help in maintaining water quality, while in HVAC systems, they are crucial for fluid circulation. As technology advances, the efficiency and application range of small pumps continue to evolve, positioning them as invaluable assets in modern engineering solutions.
Small Pumps in Various Applications
Applications of Small Pumps in Household Use
Small pumps play a crucial role in various household applications, primarily focused on moving, removing, and managing water. From transferring water during gardening to dewatering basements, these pumps are essential for efficient home maintenance. For instance, a submersible pump can be used to eliminate excess water in flooded areas, while transfer pumps help move water from one location to another, such as draining a pond or filling a pool.
Tips for optimizing pump usage include ensuring the proper size pump is selected for each job, as using an oversized pump can lead to unnecessary energy consumption, while an undersized pump may fail to deliver sufficient water flow. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can prolong the lifespan of the pump and enhance its performance.
Moreover, the market for household pumps continues to grow, driven by advancements in technology and a rising demand for efficient water management in homes. Charged with versatility, the inflatable pumps are becoming increasingly popular not just for car tires but also for sports equipment and recreational items, underlining the expanding usage and importance of small pumps in daily life.
Industrial Applications of Small Pumps in Manufacturing
Small pumps play a crucial role in various industrial applications, particularly in the manufacturing sector. The global market for hydraulic metering pumps is projected to reach approximately $874.32 million by 2025 and grow to around $1.57 billion by 2035, indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.0%. These pumps are essential in processes requiring precise fluid management, making them indispensable in industries like automotive manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food production.
In recent discussions around advanced manufacturing, the 2025 National Manufacturing Power Construction Forum highlighted the importance of innovation in creating resilient industrial clusters. Companies are increasingly investing in variable frequency drives (VFDs), which are expected to expand from a market value of $159.18 million in 2025 to $2.05 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 2.9%. VFDs improve energy efficiency and control, leading to enhanced performance of small pumps in various applications.
Tip: When selecting a small pump for your application, consider not only the flow rate and pressure requirements but also the compatibility with the fluid being pumped. Proper assessment ensures optimal performance and longevity of the pump system.
Furthermore, the inflatable pump market continues to expand, serving diverse sectors such as automotive, sports, and agriculture. With the rising demand for portable and efficient inflation solutions, manufacturers are presented with significant opportunities to innovate and strengthen their product offerings, contributing to a more dynamic market landscape.
Tip: Regular maintenance and monitoring of small pumps are vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring reliability across manufacturing operations. Implement a routine check-up schedule to keep your systems running smoothly.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Small Pumps
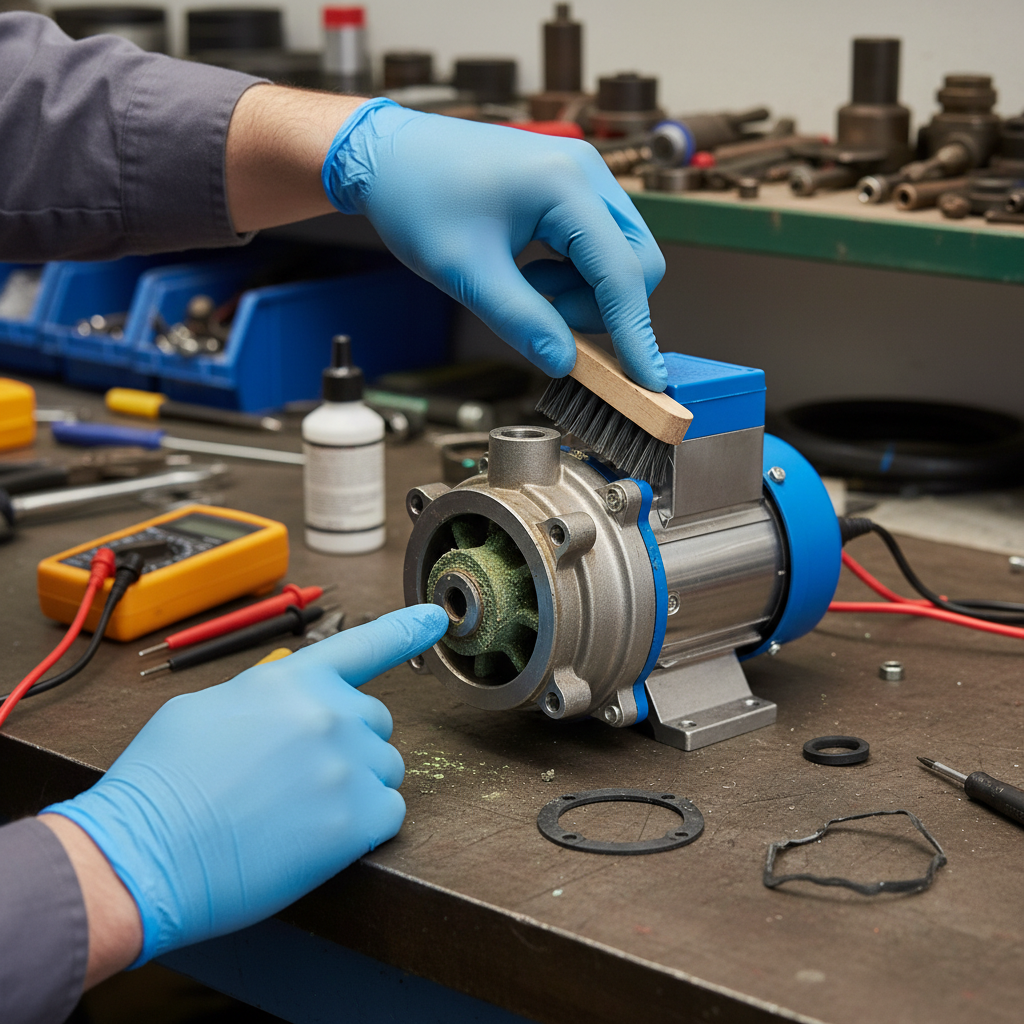

Maintaining small pumps is crucial to ensure their longevity and optimal performance across various applications. Regular inspections and cleaning can help prevent buildup that might impede functionality. Check for any visible signs of wear on seals and gaskets; these components are often the first to show signs of age. Additionally, be sure to verify electrical connections and ensure that all fasteners are tightened to avoid any operational disturbances.
Tips: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance schedules and procedures. Keeping a maintenance log can help track service history and identify recurring issues.
When troubleshooting small pumps, it’s vital to first identify any abnormal noises or vibrations during operation, as these may indicate mechanical issues. Ensure that the pump is properly primed, as a lack of fluid can lead to overheating and potentially catastrophic failure. If the pump fails to start, checking the power supply and any control systems may provide insight into electrical faults.
Tips: Consider using a multimeter to check voltage levels and ensure they meet the pump's requirements. Regularly update your troubleshooting procedures based on findings to streamline future maintenance efforts.
Related Posts
-

Top 5 Best Water Suction Pumps for Efficient Water Removal in 2023
-

Top 7 Benefits of Using Electric Water Pumps for Home and Garden Efficiency
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Flood Pump for Your Home Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Water Pump for Home Use: A Comprehensive Guide for Homeowners
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding How Water Pumps Transform Our Daily Lives
-

Top 5 Drainage Pumps for Efficient Water Removal: A Comprehensive Buyer’s Guide